Italian hospital enhances stereotactic capabilities with QA partnership

Clinicians reap the benefits of exceptional accuracy and more precise QA in less time with combination of Versa HD, Monaco and myQA
Stereotactic radiotherapy’s potent, therapeutic doses can give clinicians the confidence that the treatment will succeed in controlling cancer using a minimal number of fractions. However, powerful SBRT and SRT delivery methods demand a higher level of quality assurance (QA) accuracy to confirm the precision of tumor targeting and avoidance of organs-at-risk (OARs), thus making the treatment both effective and safe.
At Tuscany’s A.O. Santa Maria Annunziata Hospital, clinicians employ their two Versa HD™ systems to perform volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) treatments, with about 20 percent of patients receiving stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) or stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS).
Alongside their Elekta linacs, medical physicist expert Serenella Russo employs IBA’s myQA SRS dosimetric solution to satisfy their high standards for SRS/SBRT treatment verification. With the combination of Versa HD delivery, Monaco® treatment planning and myQA, the team has greater confidence when treating complex cases, such as multiple brain mets SRS cases and SBRT spine treatments that require ultra-precise targeting and OAR avoidance.
“We’ve benefited significantly from the Elekta-IBA partnership because it gives our physics staff access to advanced instrumentation during both pre-clinical and clinical phases.”
“We’ve benefited significantly from the Elekta-IBA partnership because it gives our physics staff access to advanced instrumentation during both pre-clinical and clinical phases,” Dr. Russo says. “For example, our Versa HD cases planned with Monaco enable high- and low-dose modulation to improve target coverage, creating steeper dose gradients and achieving superior dose falloff. The interoperability enables us to perform dosimetric controls with very high accuracy. Moreover, this allows reduced times for the clinical implementation of advanced techniques such as SRS and SBRT.”
She points out that PSQA traditional methods include detectors array and film. Although films offer excellent precision for dose resolution, they are not easy to use, time-consuming and tricky due to uncertainties in handling, calibration, and development. Conversely, 2D diode arrays and ion-chamber arrays generate results rapidly but they lack the necessary spatial resolution and error-detection sensitivity for SRS/SBRT QA.
“With myQA, the accuracy versus efficiency trade-off no longer applies,” Dr. Russo says.
Impressive results for multiple brain mets treatments
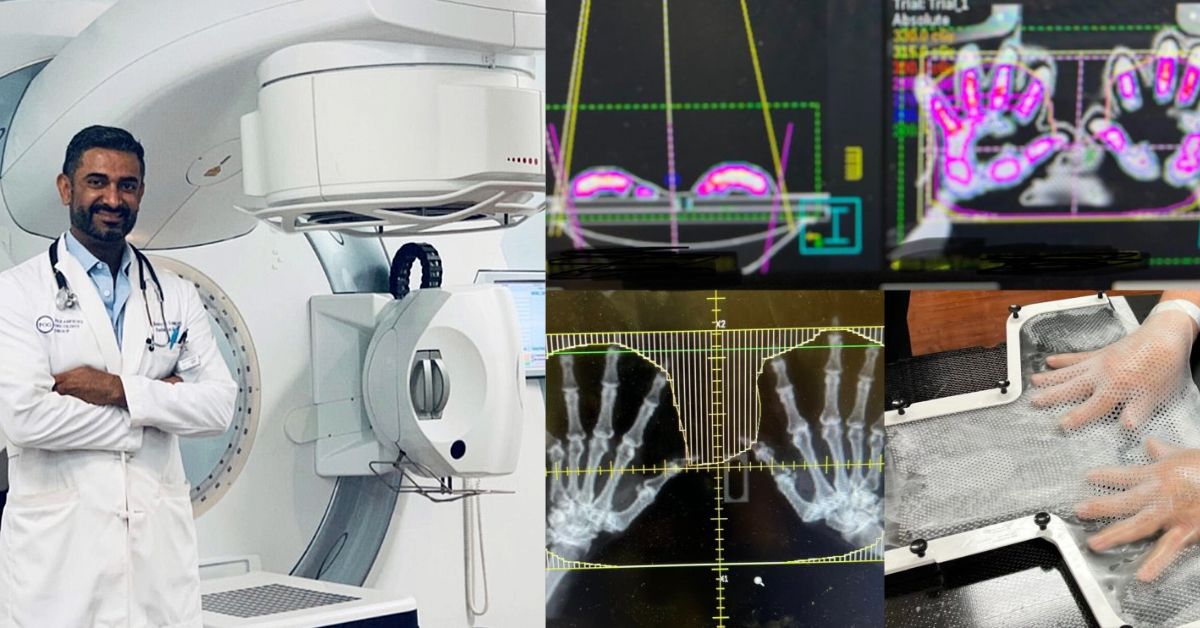
The pretreatment QA of a recent SRS multiple brain metastases case (Figure 1) with a single isocenter plan performed by myQA was particularly satisfying, according to Dr. Russo.
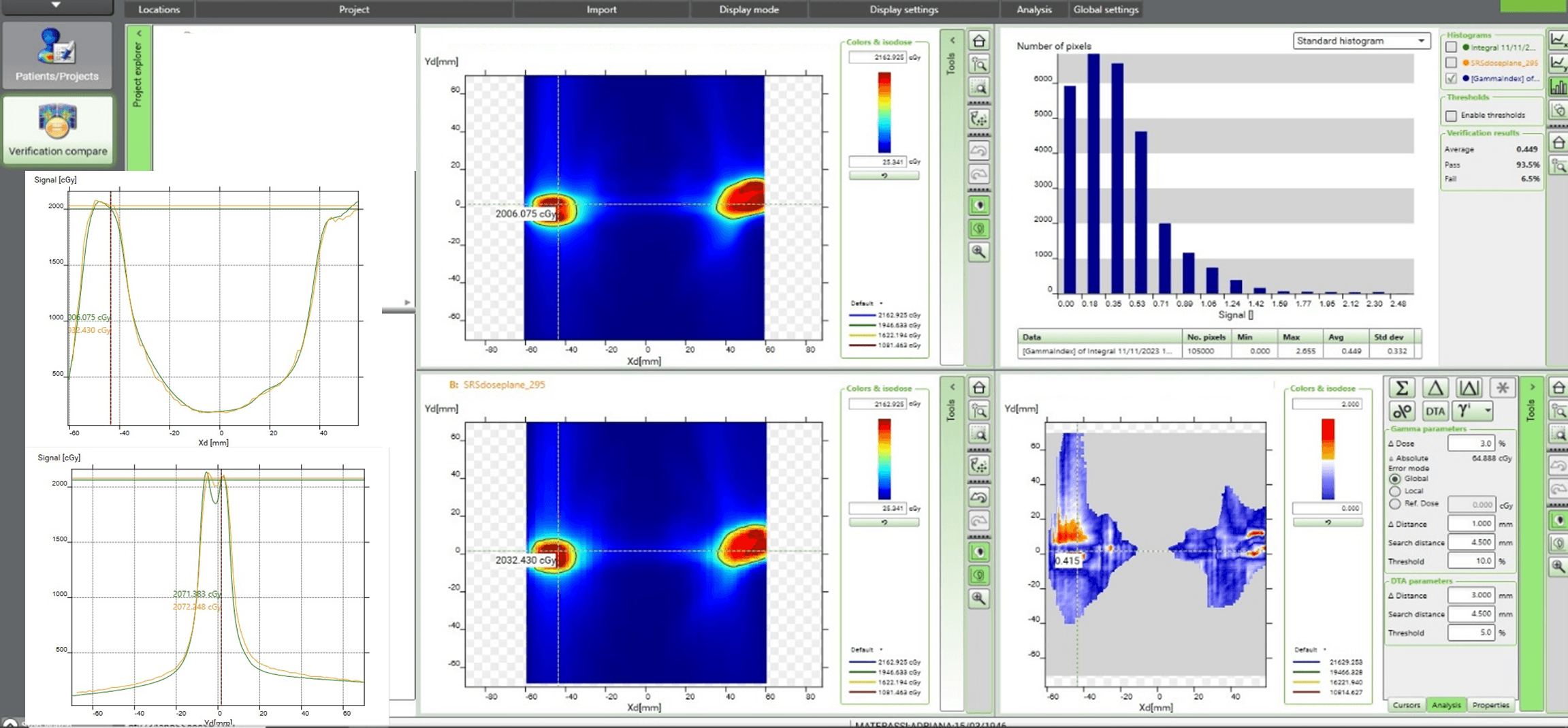
“We obtained an agreement between the measured and calculated dose distribution of 96.4 percent with a global gamma criterion of 3%/1 mm,” she says. “It is worth noting that, as recommended in the literature1, the dose difference/distance to agreement [DD/DTA] criteria should be tailored to the available instrument and to the clinical practice. In the case of SRS/SBRT treatments, it is always advisable to use the smallest possible DTA and adapting the DD accordingly.”
Dr. Russo adds that for high resolution instruments such as the myQA system, a narrow DTA (e.g., 1 mm) can be accompanied by a relaxed DD (e.g., 3%), as suggested by the recent literature.
myQA confirms exceptional targeting and maximum OAR avoidance in SBRT case
According to Dr. Russo, high-definition SRS with Versa HD and Monaco has evolved toward modulation for high and low doses to reproduce the gradients of dedicated devices, such as robotic SRS systems.
“The increased use of modulation requires more sophisticated QA tools.”

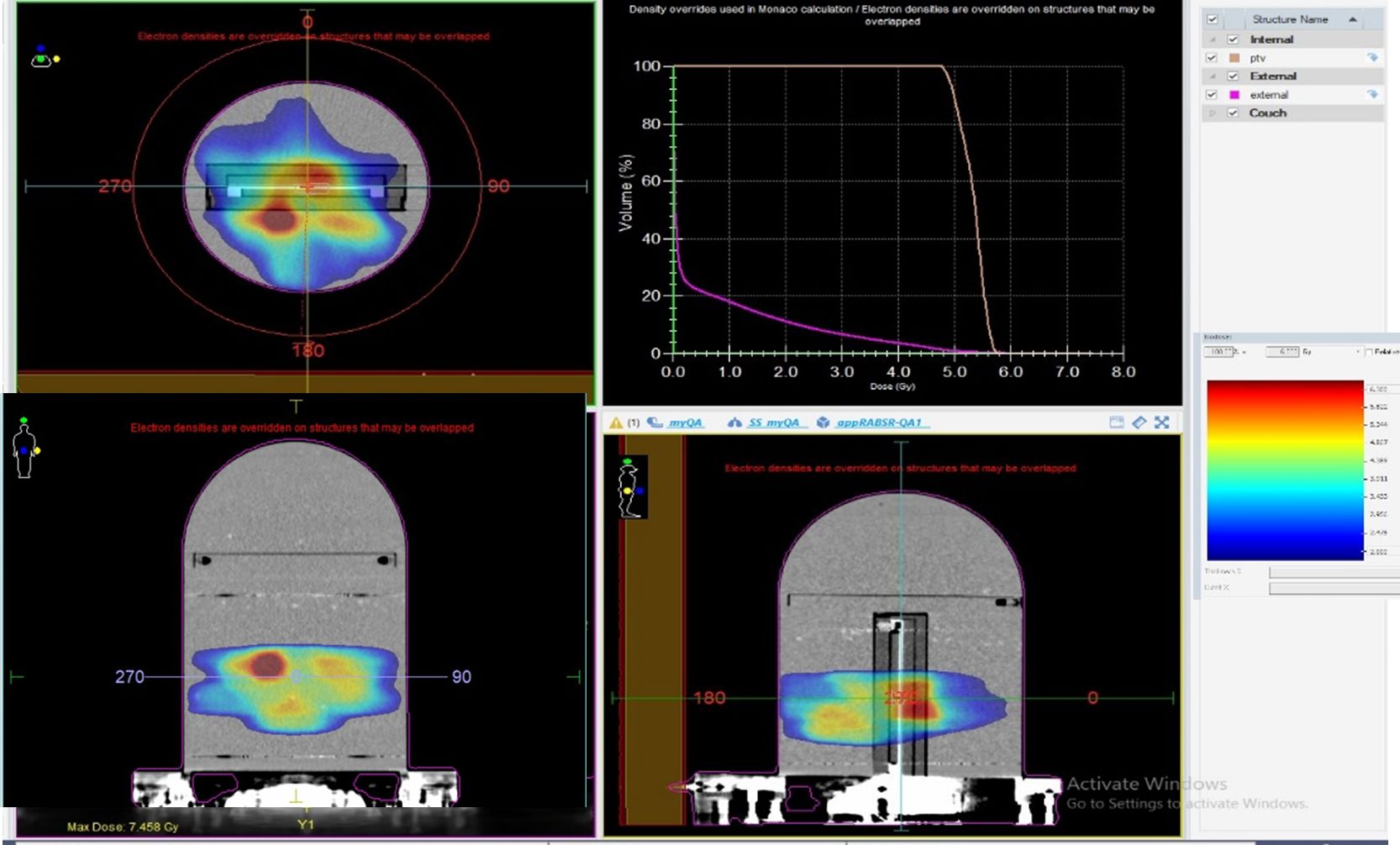
“The increased use of modulation requires more sophisticated QA tools,” she says. “We planned an SBRT spine treatment [Figures 2-3] with a boost region close to the spinal cord by using the multi-criterial optimization option in Monaco, and we managed to meet the dose constraints on the spinal cord.
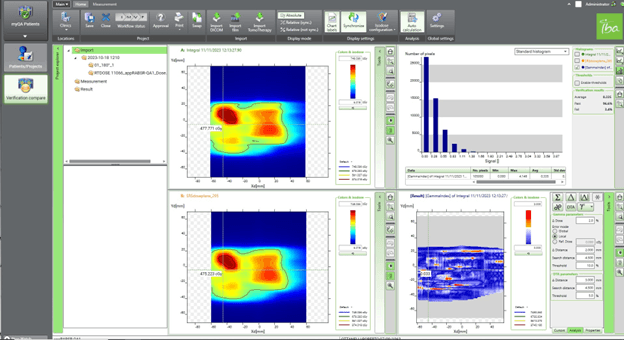
“The myQA system,” Dr. Russo continues, “allowed us to perform the pretreatment dosimetric verification with an even higher resolution than the TPS calculation grid, which is fundamentally important in this case given the proximity of the target with the most critical organ-at-risk, the brain.”
Click here to view a webinar on how Dr. Russo and her team plan SRS and SBRT cases.LAROX240806